Histamine intolerance
April 14, 2024
There are many theories you may come across when searching for explanations for an upset stomach. A less common cause is histamine intolerance. Histamine is a natural substance involved in all allergic reactions and helps the immune system defend itself against foreign substances. When histamine is released, symptoms can arise that are sometimes mistaken for IBS.
Lack of enzymes, not allergies
Histamine intolerance is not classified as an allergy because it occurs when the body absorbs too much histamine from food. This is due to a deficiency, or reduced production, of the enzyme diamine oxidase, known as DAO, which breaks down histamine. It’s the same principle as lactose intolerance. The body is unable to handle and break down the histamine already present in food or triggered by certain foods. Only one to two percent of the world’s population completely lack the DAO enzyme, but more people may have temporarily reduced production, for example, when the gut is imbalanced.
Diffuse symptoms
Symptoms such as increased heart rate, palpitations, a drop in blood pressure after meals, headaches, migraines, digestive issues, eczema, itching, or redness can be signs of histamine intolerance. It is relatively difficult to get a diagnosis of histamine intolerance within the healthcare system, even though it is possible to measure your DAO levels. Therefore, the solution may be to personally try reducing the intake of histamine-releasing foods for a period of time.
Belly Balance digital treatment
Histamine in foods
Histamine is naturally present in certain foods. However, how food is handled also affects histamine levels. For example, long storage, high temperatures, and poor hygiene increase histamine in food.
Examples of histamine-rich foods:
- Various types of aged cheeses
- Mackerel
- Tuna
- Anchovies
- Sardines
- Red wine
- Aged meat products such as salami, sausages, and smoked ham
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Sauerkraut
- Soy sauce
There are also foods that seem to release histamine in the body without showing a classic IgE reaction:
- Milk
- Pineapple
- Citrus fruits
- Chocolate
- Fish
- Pork
- Strawberries
- Papaya
- Shellfish
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Egg whites
As you can see, MANY foods are restricted, but just because they are on the list doesn’t always mean they won’t work for you—it’s important to experiment. Also, remember that knowledge about histamine intolerance, its symptoms, and treatment is not yet fully evidence-based, so don’t hesitate to seek help from a dietitian if you’re unsure.
Histamine and FODMAP
Histamine intolerance has nothing to do with FODMAP; rather, it’s a condition where the body lacks an enzyme. If you have digestive issues and aren’t improving or fully recovering with FODMAP, it may be worth testing for histamine intolerance. A tip is to try low-FODMAP foods from the histamine list; otherwise, you risk not knowing where the symptoms are coming from. Foods that generally work well for those combining a low-FODMAP diet with a low-histamine diet include rice, quinoa, gluten-free pasta, buckwheat, spelt sourdough bread, oats, blueberries, and eggs.
Sofia Antonsson
Reg. Dietitian, Belly Balance
Read more about

IBS - What is it?
Bloated , constipated or having a gassy stomach? IBS or Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a functional gastrointestinal disorder, meaning no physical issues can be found in the stomach or intestines; they just don’t function quite as they should.
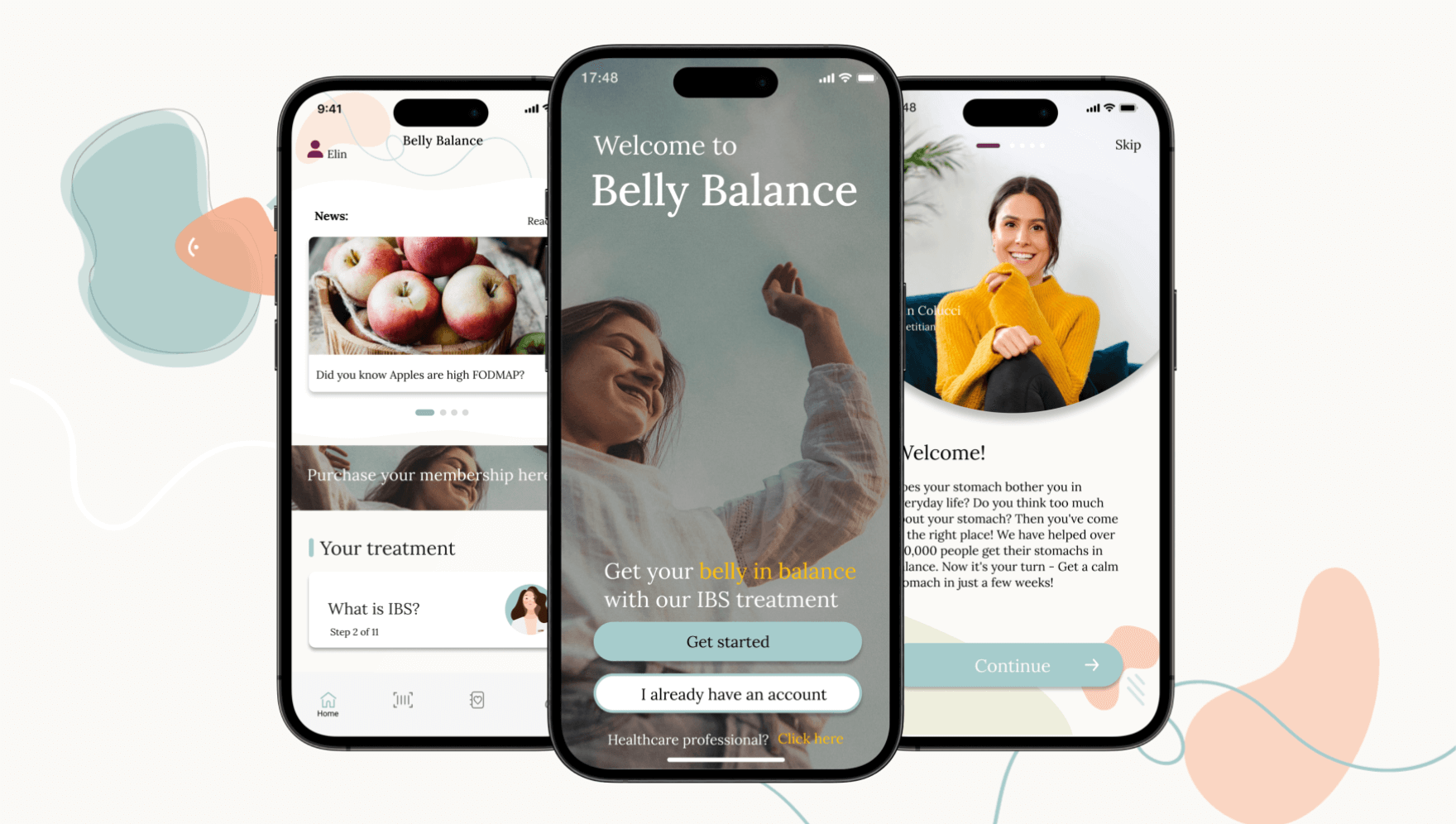
How the app works
Download the app and become part of our community. We assist you in achieving a calm and happy stomach through treatment and tools available directly in the app.

About FODMAP
By learning which foods upset your stomach, you can make conscious choices and get quick symptom relief. With the low FODMAP diet, you receive structured assistance in understanding which foods your body tolerates better than others. No more guessing and pondering – you get the answer straight away!